Home > Our Products > English Assessments > Writing Test
G-TELP Writing Test
The G-TELP Writing Test is a measure of general English language writing proficiency.
Take a Practice Test
Register
The G-TELP Writing Test is designed to assess the general English writing proficiency of non-native English speakers, developed by the evaluation experts at International Testing Services Center (ITSC).
| Test Type | Simulated Writing Proficiency Test |
|---|---|
| Duration | Approximately 60 minutes |
| Availability of Score Report | Seven working days |
| Questions | Five questions corresponding to five parts |
| Levels | Levels 1 to 11 |
| Criteria | Grammar, Vocabulary, Organization, Style, Substance |
| Duration of Score Validity | Two years |
With the globalization of business and liberalization of foreign travel, there is a fast-growing and compelling need for non-native English speakers to write better English for their day-to-day interactions. They need to enhance their English-language writing skills to effectively communicate not only with their English-speaking peers in their country but also with both native English speakers and non-native English speakers in various parts of the world. This need has become even more acute with the growing use of the internet, where English is internationally accepted as the language for communicating information, ideas, thoughts, and feelings. Electronic mail and chat rooms have intensified this communication exchange at even greater speeds, and in ways that demand clear and immediate responses.
Therefore, there is a need for a formally administered test that can measure the level of a non-native speaker's practical English writing proficiency, and whose results can serve as a progressive basis for improvement.
ITSC created the G-TELP Writing Test to evaluate non-native English writers' ability to use written English in everyday situations. This assessment can help non-native speakers improve their English writing skills and build their confidence.
The G-TELP Writing Test complements the General Tests of Language Proficiency (G-TELP™) in assessing the English proficiency of non-native English speakers. Together, these tests form a powerful battery of measuring tools that can help people achieve higher levels of proficiency in the English language.
Therefore, there is a need for a formally administered test that can measure the level of a non-native speaker's practical English writing proficiency, and whose results can serve as a progressive basis for improvement.
ITSC created the G-TELP Writing Test to evaluate non-native English writers' ability to use written English in everyday situations. This assessment can help non-native speakers improve their English writing skills and build their confidence.
The G-TELP Writing Test complements the General Tests of Language Proficiency (G-TELP™) in assessing the English proficiency of non-native English speakers. Together, these tests form a powerful battery of measuring tools that can help people achieve higher levels of proficiency in the English language.
Format
| Part | Task | Response Time (minutes) |
|---|---|---|
| Part 1 | Constructing a Paragraph | 6 |
| Part 2 | Composing a Personal Letter | 12 |
| Part 3 | Composing a Formal Letter | 12 |
| Part 4 | Describing a Situation | 14 |
| Part 5 | Writing an Essay | 16 |
The G-TELP Writing Test assesses the facility and proficiency of non-native English speakers' English written communication.
It is a highly useful writing test in that:
- It closely approximates a measure of communicative competence in writing because it simulates real-world situations.
- It is a measure of general English language writing proficiency, rather than being specifically geared to academic or business contexts (e.g., for academic study in institutions of higher education in North America).
- Its criteria are derived from experience regarding the acquisition of English language writing skills by non-native speakers, regardless of any particular cultural context or specific testing purpose.
Users of the Writing Test
The G-TELP Writing Test can be used by the following:
- Students of all schools, colleges, universities and technical schools
- Students expecting to attend schools where English is the medium of instruction
- Students in technical training institutions
- Individuals in organizations that provide employee training
- Individuals such as teachers and students who are studying English
- Translators whose work requires the written communication of authentic English texts, speeches, or media broadcasts
- Professionals and employees who need varying levels of English oral proficiency to perform their work
- Employees of government agencies and businesses that require certain levels of English oral proficiency for specific positions
- Tourists planning to visit English speaking countries
These tasks simulate real-life activities, such as school assignments, work, reports, cultural articles, scientific journals, media ads, and personal letters. Each writing task gives examinees the opportunity to develop and organize ideas in response to a set of requirements, and to express those ideas in English.
The G-TELP Writing Test is composed of five parts. Each part requires examinees to write compositions in response to specific situations and questions.
The G-TELP Writing Test is composed of five parts. Each part requires examinees to write compositions in response to specific situations and questions.
| Part | Tasks | Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Part 1 | Constructing a Paragraph | The examinee is required to Compose a paragraph based on the title provided. The ideas and details provided by the examinee must be both appropriate and directly related to the title, and the paragraph should be composed of at least six sentences, with each sentence containing one of the keywords provided in the directions. |
| Part 2 | Composing a Personal Letter | The examinee is required to compose a personal email in response to a given scenario. The email must be addressed to the person indicated in the scenario, and must include all the information provided in the scenario. The examinee must also be able to include an appropriate subject, greeting, and closing. |
| Part 3 | Composing a Formal Letter | The examinee is required to compose a formal letter in response to a given scenario. The letter must include all the information provided in the scenario, and the examinee must provide additional information or detail to further develop and explain the main idea of the letter. Lastly, the examinee must be able to include an appropriate subject, greeting, and closing. |
| Part 4 | Describing a Situation | The examinee is required to write a detailed article about the information presented in a graph, chart, or table. The examinee should create an appropriate title for the article, and must be able to give an example of an event or a situation that could possibly happen or occur as a result of the information depicted in the graph. Lastly, the example of the event or situation must be described in detail, and should be based on the information provided by the graph. |
| Part 5 | Writing an Essay | The examinee will be presented with a topic. The examinee will be required to compose an essay on the topic. The essay must include a clear statement of the examinee's opinion on the topic, and the examinee must provide sufficient detail to explain and justify his or her opinion. |
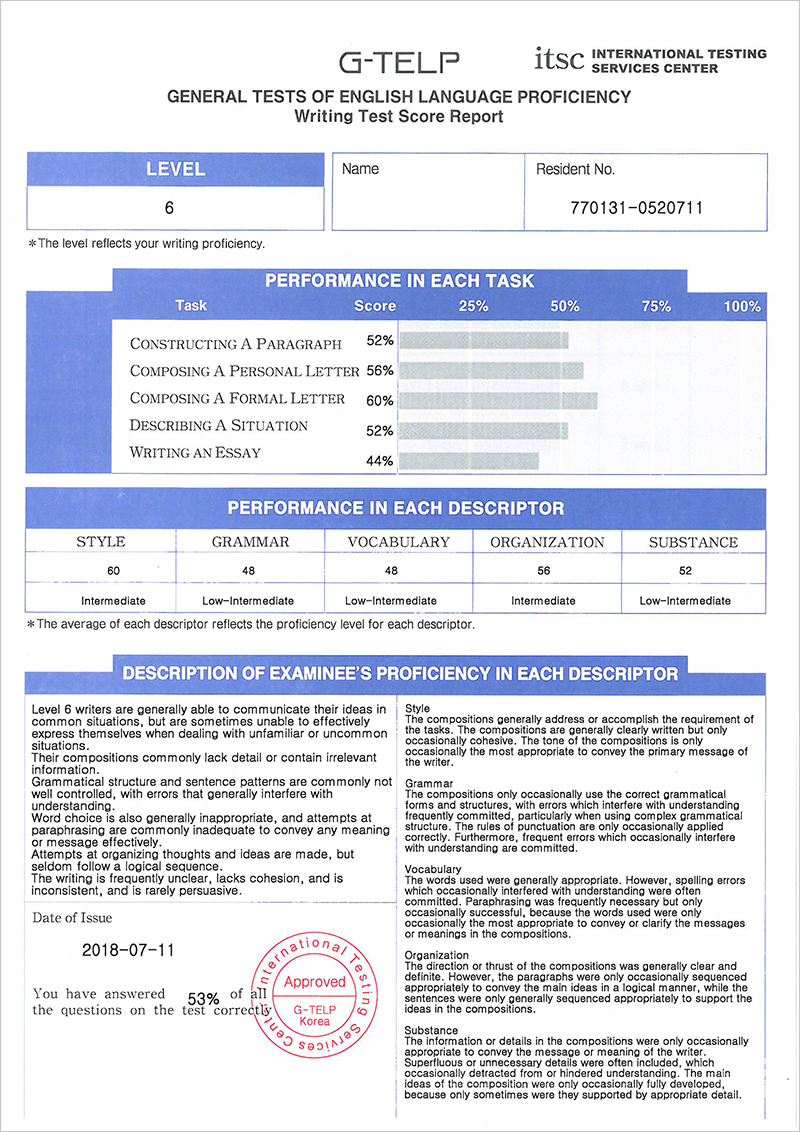
Each examinee receives a Score Report that includes several scores: the Mastery Level; Level Scores for each part; percentage profiles indicating performance on each task; and evaluations of performance on the descriptors (Style, Grammar, Vocabulary, Organization, Substance) across all five parts.
Skill Area Score
The Skill Areas are defined as the following:
- Style: The raters evaluate cohesiveness and clarity of the writing, along with how persuasive the composition was.
- Grammar: The raters evaluate the degree to which the examinee applies the correct grammatical structures, sentence patterns, and rules of punctuation.
- Vocabulary: The raters evaluate the degree to which the examinee uses the appropriate English words or terms, and the extent and precision of the terminology used.
- Organization: The raters evaluate the degree to which sentences and paragraphs maintain a logical progression of ideas from the initial presentation to the conclusion.
- Substance: The raters evaluate the degree to which topics are established and ideas and messages are developed.
Release of Test Results
The results will be released no later than eight working days after the test date on the G-TELP website. The original score report will be printed out or mailed out directly to test-takers within two weeks of the test date.
Validity of Test Results
A score report will not be reissued if two years have passed since taking the test because English proficiency may improve or decline over time.
The G-TELP Writing Test assesses the English writing proficiency of non-native English speakers and forms a powerful battery of measuring tools that can help people achieve higher levels of proficiency in the English language.
Level Description
Level 1 : Authentic
Level 1 writers are able to express themselves with ease in all situations, whether familiar or unfamiliar. Their vocabulary is wide and varied, with word choice being consistently appropriate and meaningful. They are able to paraphrase accurately, and use idiomatic expressions appropriately. They display consistent and accurate use of grammatical structure, sentence patterns, and word order. They address the writing task effectively by elaborating on ideas and citing details or specific examples. Thoughts and ideas are organized in a logical, sequenced manner which makes it easy to determine the meanings or messages of the composition. Their writing is clear, consistent, cohesive, and persuasive.
Level 2 : Highly Advanced
Level 2 writers are able to communicate their ideas effectively in nearly all situations. Their writing is marked by the use of detail to create appropriate and informative passages. Grammatical structure and sentence patterns are usually well controlled, with only rare errors that almost never interfere with meaning. They display a wide vocabulary and are able to paraphrase consistently and effectively. Their writing is organized, with thoughts and ideas laid out in a logical manner. It is almost always clear, consistent, and cohesive, and is generally persuasive
Level 3 : Advanced
Level 3 writers are usually able to communicate their ideas effectively and create compositions that are appropriate and informative. Grammatical structure and sentence patterns are usually well controlled, with some errors, although these seldom interfere with meaning. They usually display appropriate word choice and the ability to paraphrase when lacking vocabulary in unusual or unexpected circumstances. Thoughts and ideas usually follow a logical sequence and demonstrate competent organization. Their writing is usually clear, consistent, and cohesive but sometimes lacks persuasiveness.
Level 4 : High-Intermediate
Level 4 writers are generally able to communicate their ideas in most situations and create compositions that are appropriate and informative. Grammatical structure and sentence patterns are generally well controlled, with errors that sometimes interfere with meaning. They generally display appropriate word choice and the ability to paraphrase when lacking vocabulary in unusual or unexpected circumstances. Thoughts and ideas are generally organized, with attempts to maintain logical sequencing. Their writing is generally clear, consistent, and cohesive but has a tendency to lack persuasiveness.
Level 5 : Intermediate
Level 5 writers are generally able to communicate their ideas in common situations but may have trouble when dealing with unfamiliar or uncommon events. Their compositions may be inappropriate or lack detail. Grammatical structure and sentence patterns are still generally well controlled, although errors are likely to interfere with meaning. They sometimes display appropriate word choice and the ability to paraphrase effectively. Thoughts and ideas are sometimes organized but can lack logical sequencing. Their writing is only sometimes clear, cohesive, and consistent, frequently lacking persuasiveness.
Level 6 : Low-Intermediate
Level 6 writers are sometimes able to communicate their ideas in common situations but often struggle to effectively express themselves when dealing with unfamiliar or uncommon situations. Their compositions commonly lack detail or contain irrelevant information. Grammatical structure and sentence patterns are often not well controlled, with errors that frequently interfere with understanding. They commonly display inappropriate word choice and paraphrasing that inadequately conveys any meaning or message. Attempts at organizing thoughts and ideas are made, but these seldom follow a logical sequence. The writing is frequently unclear, lacking in cohesion, and inconsistent. It is rarely persuasive.
Level 7 : High-Basic
Level 7 writers generally have a difficult time communicating their ideas in common situations, and this problem becomes more serious when they attempt to express unfamiliar or uncommon situations. Their compositions usually lack detail or contain irrelevant or inappropriate information. Grammatical structure and sentence patterns are often inappropriate, with errors that usually interfere with understanding. They frequently display inappropriate word choice and an inability to paraphrase effectively. Thoughts and ideas have no discernible organization and very rarely follow a logical sequence. The writing is very often unclear, lacking in cohesion, and inconsistent. Level 7 writers are almost never persuasive.
Level 8 : Basic
Level 8 writers usually have a difficult time expressing their ideas in common situations and are frequently unable to effectively respond when dealing with unfamiliar or uncommon situations. Compositions frequently lack detail and contain a lot of irrelevant or inappropriate information. Frequent grammatical structure and sentence pattern errors are made, almost always interfering with understanding. Word choice is very often inappropriate and confusing, and attempts at paraphrasing usually fail. Thoughts and ideas are scattered haphazardly. The writing is almost always unclear, inconsistent, and lacking in cohesion and persuasiveness.
Level 9 : Low-Basic
Level 9 writers frequently have a difficult time communicating their ideas in common situations and are almost always unable to effectively respond when dealing with unfamiliar or uncommon situations. Compositions almost always lack detail and contain a lot of irrelevant and inappropriate information. Grammatical structure and sentence patterns are almost always uncontrolled, with serious errors that almost always interfere with understanding. Word choice is inappropriate for the most part, and attempts at paraphrasing almost always fail. The lack of logic and sequencing of the thoughts and ideas makes it extremely difficult to understand the message or meaning that the composition is supposed to convey.
Level 10 : Beginner-Basic
Level 10 writers almost always have a difficult time expressing their ideas, even in common or familiar situations. Compositions almost always lack even basic detail and are filled with irrelevant and inappropriate information that prevents readers from determining the purpose of the writing. Grammatical structure and sentence patterns are uncontrolled, which always interferes with understanding. Word choice is almost always inappropriate, with no attempts at paraphrasing. The absence of any organization or sequencing of thoughts and ideas prevents readers from understanding the composition.
Level 11: No Mastery
Level 11 writers may exhibit a vocabulary of a handful of memorized words and isolated phrases only. They are unable to express themselves in a meaningful way.
